All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the Lymphoma Coalition.
The lym Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lym Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lym and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lymphoma & CLL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AbbVie, BeOne Medicines, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Nurix Therapeutics, Roche, Sobi, and Thermo Fisher Scientific and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, and Pfizer. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lymphoma & CLL content recommended for you
AACR 2017 | Poster 2444/1 – Recurrent mutations and clinical outcomes in patients with Follicular Lymphoma
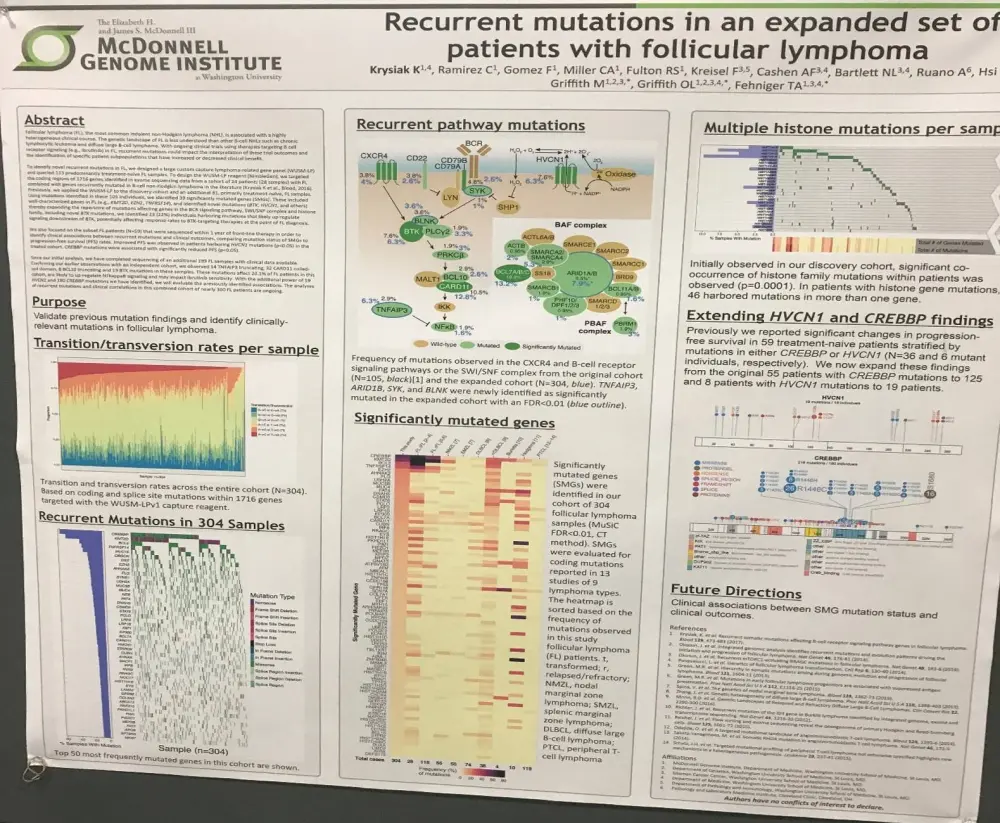
On Monday 3rd April during this year’s American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) annual meeting, a poster (2444 / 1) by Kilannin Krysiak, from Washington University, St. Louis, MO, et al. titled “Recurrent mutations and clinical outcomes in patients with follicular lymphoma” was presented.
The group aimed to validate previously found mutations and to identify clinically relevant mutations in FL. They designed a large, custom capture lymphoma-related gene panel and queried 113 samples from mostly newly diagnosed FL patients.
Key Highlights:
- From 105 patients, 39 significantly mutated genes (SMGs) were identified
- This included previously known genes in FL: KMT2D, EZH2, TNFRSF14
- Identified novel mutations: BTK, HVCN1
- 110 CREBBP mutations
- Significant co-occurrence of histone family mutations reported (P = 0.0001); 46 patients harbored >1 histone family mutation
- Twenty-three patients (22%) had genetic aberrations likely to up-regulate signaling downstream of BTK, possible altering response rates to BTK-specific therapy
- In patients sequenced within 12 months of first-line therapy (n = 59), those with HVCN1 mutations had improved PFS (P < 0.05) whereas those with CREBBP mutations had a significantly poorer PFS (P < 0.05)
- Sequencing of an additional 199 FL samples found 14 TNFAIP3 truncating, 18 CARD11 coiled-coil domain, 4 BCL10 truncating, and 8 BTK mutations
- These mutations affected 18.4% of patients in this cohort, and potentially upregulate NFkB signaling and may impact ibrutinib sensitivity
The poster was concluded by stating that future work should be undertaken to determine the associated between SMGs and clinical outcomes.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content

