All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the Lymphoma Coalition.
The lym Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lym Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lym and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lymphoma & CLL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AbbVie, BeOne Medicines, Johnson & Johnson, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Nurix Therapeutics, Roche, Sobi and Thermo Fisher Scientific and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly and Pfizer. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lymphoma & CLL content recommended for you
Outpatient administration of liso-cel: Preliminary results from the OUTREACH study
Due to concerns regarding adverse events (AEs), chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies are predominantly given as inpatient treatments in university medical centers in the U.S. However, the necessity of this limitation, and the safety of administering CAR T-cell therapies in outpatient and nonuniversity settings, has not yet been examined.
During the 47th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT), John Godwin presented preliminary data from the OUTREACH study (NCT03744676), an open-label, multicenter, phase II study of safety and efficacy outcomes of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in relapsed/refractory (R/R) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) in nonuniversity inpatient and outpatient settings in the U.S. We are pleased to report a summary of the findings here, which expand upon the initial results previously covered on the Lymphoma Hub.
Study design
Following lymphodepletion with fludarabine 30 mg/m2 and cyclophosphamide 300 mg/m2 for 3 days, adults with R/R LBCL received liso-cel at 100 × 106 CAR T cells, 2–7 days after lymphodepletion, either as inpatients or outpatients at nonuniversity medical centers.
Eligible patients had R/R positron emission tomography (PET)-confirmed disease after ≥2 lines of therapy, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS) ≤1, and adequate organ function. Prior autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplants (HSCTs) were permitted, as were secondary central nervous system lymphomas.
Primary endpoints were incidences of Grade ≥3 cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurologic events (NEs), prolonged cytopenias, and infections. Secondary endpoints included AEs, overall response rate (ORR), and complete response (CR) rate.
Patients
Of the 46 patients enrolled, 43% and 50% of outpatients and inpatients, respectively, were aged ≥65 years. Patient characteristics in both settings are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Characteristics of patients enrolled in outpatient and inpatient settings1
|
DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; FL3B, follicular lymphoma Grade 3B; HGBCL, high-grade B-cell lymphoma; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplant; NOS, not otherwise specified; PMBCL, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. |
||
|
Outcome |
Outpatients |
Inpatients |
|---|---|---|
|
Median age, years (range) |
63 (35–83) |
65 (34–81) |
|
Male, % |
70 |
63 |
|
Ethnicity, % |
|
|
|
Histology, % |
|
|
|
ECOG PS ≤1, % |
100 |
100 |
|
Median prior lines of therapy, n (range) |
2 (2–4) |
2 (2–6) |
|
Prior HSCT, % |
27 |
6 |
|
Chemotherapy refractory, % |
83 |
88 |
Key findings
Safety
The most common treatment-emergent AEs (TEAEs) in outpatient and inpatient settings were neutropenia, leukopenia, and anemia. Cytopenias were less frequent in outpatients versus inpatients (neutropenia, 57% vs 94%). Table 2 lists TEAEs of special interest. No cases of CRS Grade ≥3 were reported in either setting, and incidences of Grade ≥3 NEs were similar. Infections and prolonged cytopenias of Grade ≥3 were more frequent in outpatients than inpatients. The use of tocilizumab with or without corticosteroids for the management of CRS (13%) and NEs (11%) was low.
Table 2. AEs of special interest reported in outpatient and inpatient settings1
|
AE, adverse event; CRS, cytokine release syndrome; NE, neurological event. |
||
|
AE |
Outpatients |
Inpatients |
|---|---|---|
|
CRS |
|
|
|
NE |
|
|
|
Prolonged cytopenia Grade ≥3, %* |
30 |
13 |
|
Infection Grade ≥3, % |
17 |
6 |
Hospitalization was required for 19 outpatients (63%) after a median time of 5 days (range, 2–61); 16 of these were due to AEs. One outpatient was admitted to intensive care following liso-cel administration.
Efficacy
After a median follow-up of 6.7 months (range, 0.4–16.0), efficacy outcomes were similar between outpatients and inpatients (Figure 1). Durable responses were observed, with ongoing CRs noted in 92% of patients with ≥6 months of follow-up data available.
Figure 1. Best overall response with liso-cel treatment in outpatient and inpatient settings1
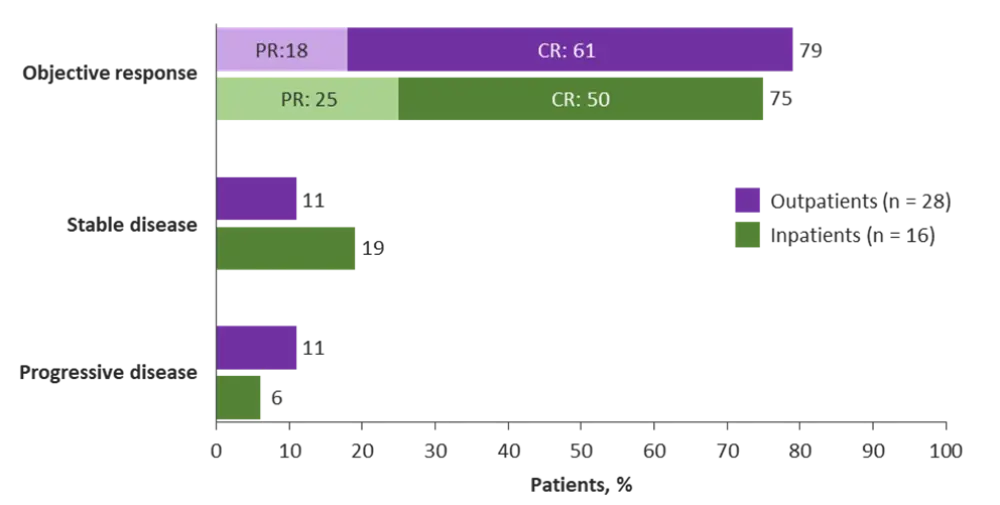
CR, complete response; PR, partial response.
Conclusion
In this study of patients with R/R LBCL, administration of liso-cel and monitoring of CAR T-cell therapy-related toxicities was feasible and effective in outpatient settings in nonuniversity medical centers, in addition to inpatient treatment. Incidences of severe CRS and NEs were low in both settings, with similar ORR and CR rates.
The authors therefore concluded that it is safe to provide liso-cel treatment in outpatient settings and nonuniversity centers, which will provide greater convenience and accessibility for patients.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content

