All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the Lymphoma Coalition.
The lym Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lym Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lym and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lymphoma & CLL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AbbVie, BeOne Medicines, Johnson & Johnson, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Nurix Therapeutics, Roche, Sobi, and Thermo Fisher Scientific and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, and Pfizer. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lymphoma & CLL content recommended for you
The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of hematolymphoid tumors: lymphoid neoplasms. Part 2
Now set to be published later this year, the upcoming 5th edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of hematolymphoid tumors (WHO-HAEM5) updates the conceptual framework and reflects major developments that have occurred in the field since 2017. This revised edition contains a restructuring of entities into a hierarchical system, updates to nomenclature, revision of diagnostic criteria or subtypes, deletion of certain entities, and introduction of new entities; the conceptual description of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) has also undergone significant change. The LBCL family is highly varied and comprises a wide spectrum of tumors, which is reflected in the new classifications; WHO-HAEM5 now recognizes 17 specific entities as LBCL other than DLBCL-not otherwise specified.1
Below, the Lymphoma Hub is happy to present part two in a series summarizing the upcoming 5th edition, published on behalf of the WHO by Alaggio et al. in Leukemia. This part focuses on updates to DLBCL in detail. Part one in our series was centered on updates and new additions to B-cell lymphoid proliferations and lymphomas, while our upcoming third and final part will address T-cell lymphoid malignancies.
Figure 1 provides a visual representation of the new hierarchical system of classification, using germinal center B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma as an example.
Figure 1. Overview of the hierarchal system of classification*
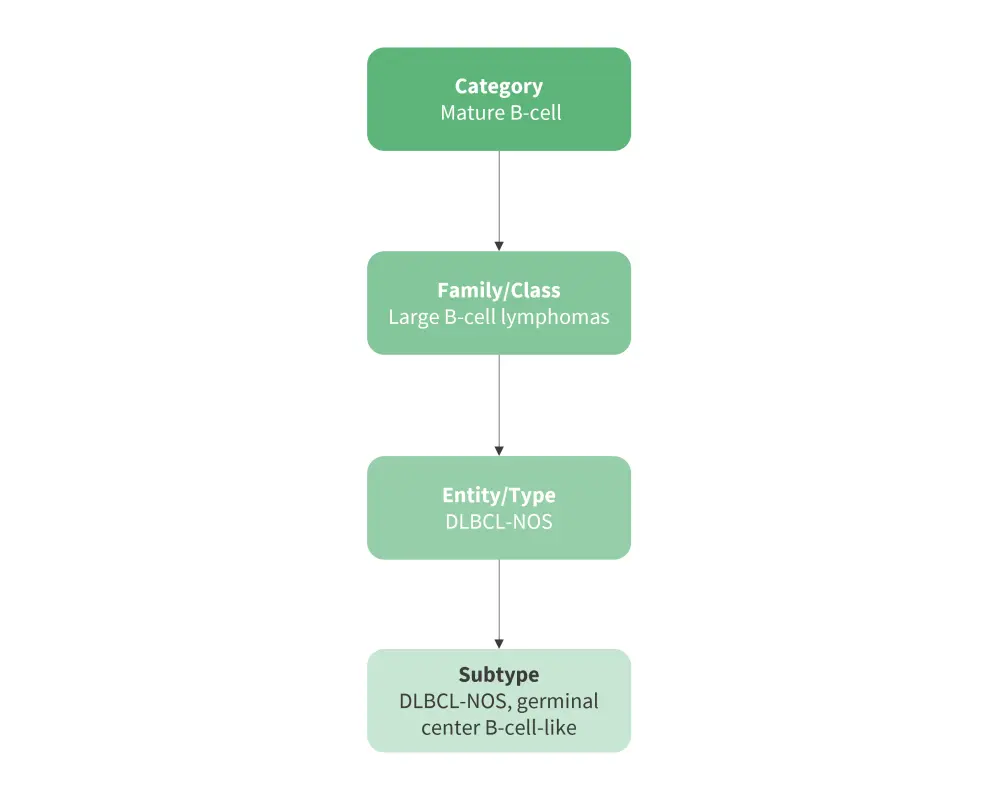
DLBCL-NOS, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-not otherwise specified.
*Adapted from Alaggio, et al.1
Figure 2 and Figure 3 provide an overview of changes and new additions in the classification of B-cell lymphoid proliferations and lymphomas.
Figure 2. Changes to DLBCL classification*
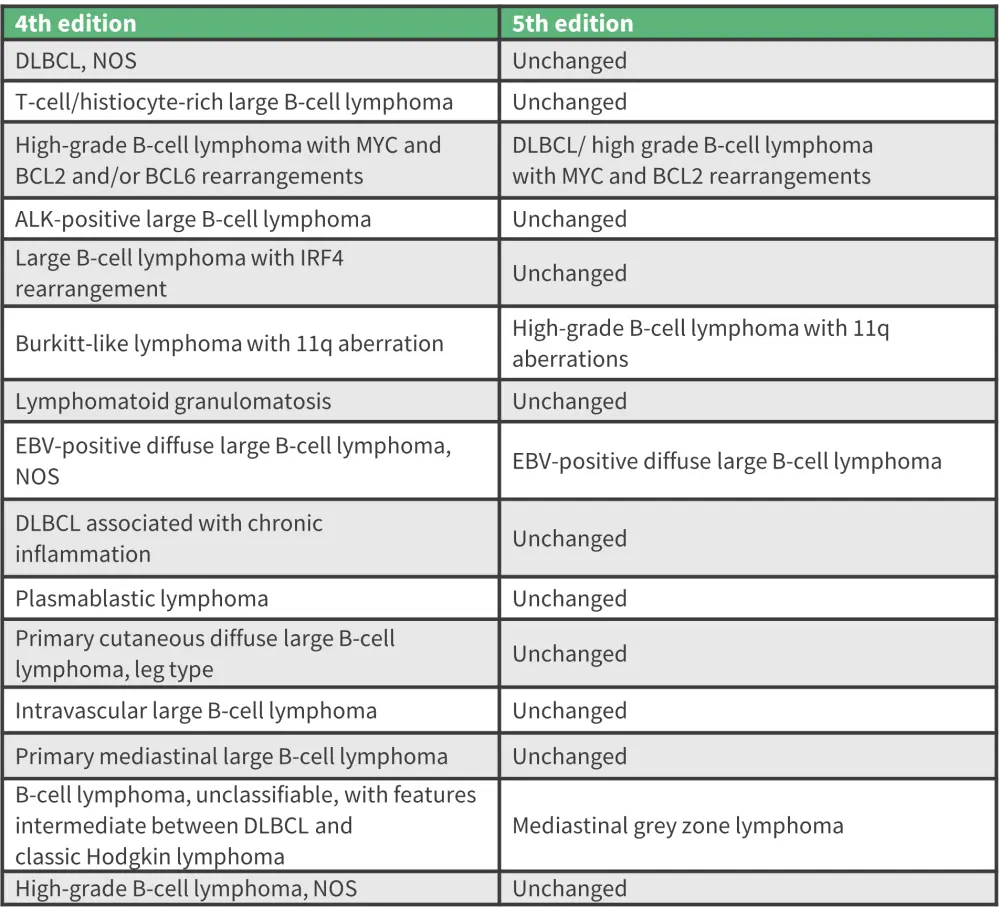
ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; NOS, not otherwise specified
*Adapted from Alaggio, et al.1
Figure 3. New additions to the DLBCL category*

CNS, central nervous system; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
*Adapted from Alaggio, et al.1
Although entities within the LBCL classification family are typically characterized by medium to large-sized cells with round to ovoid nuclei and vesicular chromatin, entities with intermediate-sized and blastoid cells may also meet criteria for this family. The need to differentiate these from morphologically similar entities is essential to maintain clarity in classification and avoid misdiagnosis.1
For most entities in the DLBCL family, biological concepts and diagnostic strategies have not undergone significant change from WHO-HAEM4R. However, some entities have been altered for consistency from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma to large B-cell lymphoma, because a diffuse growth pattern is not present or detectable in some entities.1
Certain entities remain difficult to classify, with some ambiguity around the most appropriate category for them. For example, rare cases of classic follicular lymphoma were previously classified as DLBCL with follicular lymphoma under WHO-HAEM4R. Currently, it is unclear whether such cases should be classified as classical follicular lymphoma or DLBCL.1
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma/high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 rearrangements1
The previously named WHO-HAEM4R entity of high-grade B-cell lymphoma with dual rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 has been revised and renamed as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma/high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 rearrangements. This has been done to include tumors defined by the presence of dual MYC and BCL2 rearrangements, which may be composed of large, intermediate, or blastoid cells. In practice, this maintains the morphological categorization of the neoplasm after determination of its genetic makeup.
High-grade B-cell lymphoma with 11q aberrations1
The entity previously known as Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration is an aggressive MYC rearrangement-negative mature B-cell lymphoma with a morphology akin to that of Burkitt lymphoma. Recent genetic analyses have demonstrated the mutational spectrum as distinct from that of Burkitt lymphoma and more similar to that of germinal center B-cell like DLBCL.
Primary large B-cell lymphomas (LBCL) of immune-privileged sites1
This is a new umbrella term that accounts for the common biological features of a group of aggressive B-cell lymphomas that arise as primary tumors in the central nervous system (CNS), the vitreoretinal compartment, and the testes of immunocompetent patients. It combines the previous classification of primary DLBCL of CNS with DLBCL of the vitreoretina and testis, which were previously included among DLBCL-not otherwise specified. Our knowledge of this tumor group is rapidly advancing, with predictions that this family of immune-privileged tumors may expand in future classifications.
Fluid overload-associated large B-cell lymphoma1
This classification represents a new addition to the family of LBCL in WHO-HAEM5, distinct from primary effusion lymphoma. It typically affects older adults without primary immunodeficiency who often have an underlying condition causing fluid overload, such as chronic heart failure, renal failure, protein losing enteropathy, or liver failure/cirrhosis.
Mediastinal gray zone lymphoma1
Mediastinal gray zone lymphoma is a new addition to the large B-cell lymphoma family, replacing the former B-cell-lymphoma, unclassifiable with features intermediate between DLBCL and classic Hodgkin lymphoma classification. It has features overlapping between primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma and classic Hodgkin lymphoma, especially nodular sclerosis classic Hodgkin lymphoma.
Conclusion
WHO-HAEM5 represents a significant overhaul of the WHO system of classification of hematolymphoid tumors. Updates to the DLBCL family of lymphomas represents this particularly well. Updates to this comprehensive classification hierarchy reflect the dramatic increase in information regarding lymphoid tumors, their molecular complexity, and advances in diagnostic techniques and understanding.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content


