All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the Lymphoma Coalition.
The lym Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lym Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lym and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lymphoma & CLL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AbbVie, BeOne Medicines, Johnson & Johnson, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Nurix Therapeutics, Roche, Sobi and Thermo Fisher Scientific and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly and Pfizer. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lymphoma & CLL content recommended for you
ASH 2016 | SAKK 35/10 first analysis of survival endpoints of rituximab combined with lenalidomide in first-line FL
The 58th Annual Meeting & Exposition of the American Society of Hematology’s (ASH) took place in San Diego, CA, on December 3–6, 2016. On Monday 5th December, an oral abstract session was held between 4:30pm and 6:00pm in the “Mantle Cell, Follicular, and Other Indolent B-Cell Lymphoma—Clinical Studies: Novel Therapy and Prognostic Markers in Follicular Lymphoma” category. This session was moderated by Frederick Lansigan, MD, of the Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, and John Kuruvilla, MD, from the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre.
Abstract #1099 was presented during this morning session, titled “Rituximab Plus Lenalidomide Versus Rituximab Monotherapy in Untreated Follicular Lymphoma Patients in Need of Therapy. First Analysis of Survival Endpoints of the Randomized Phase-2 Trial SAKK 35/10” by Eva Kimby, MD, from the Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden, and colleagues.
SAKK 35/10 is a randomized, phase II trial by the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research (SAKK) and the Nordic Lymphoma Group (NLG) comparing single-agent rituximab and rituximab plus lenalidomide as first-line treatment for symptomatic grade 1–3a FL. During this talk, the first analysis of PFS, Time To Next Anti-Lymphoma Treatment (TTNT), CR duration, and CR/CRu rate at 30 months (CR30) was presented. Seventy-seven patients with a median age of 63 years, 52% with stage IV and 47% with poor-risk FLIPI score, were assigned to the single-agent rituximab arm. A further 77 patients with a median age of 61 years, 48% stage IV and 47% poor-risk FLIPI score, were allocated to the combination arm.
Highlights:
- Higher CR/CRu rate was reported in the combination arm by the investigator assessment and by independent response reviewers of CT scans (36% vs 25%; 61% vs 36%)
- Grade ≥3 adverse events were more frequent in the combination arm compared to the single-agent arm (56% vs 22% patients), including neutropenia (23% vs 7%)
- At a median follow-up of 3.1 years, a longer CR duration and PFS was reported in the combination arm (median not reached and median not reached) compared to the single-agent arm (2.3 years and 2.3 years); these differences were not statistically significant
- CR30 was significantly improved by combining rituximab with lenalidomide (42% vs 19%, p=0.001)
- TTNT was significantly longer in the combination arm (median not reached) compared to the single-agent arm (2.1 years; p=0.02)
- 3-year OS rates were 93% and 92% for the combination and single-agent arms, respectively
This presentation concluded by stating that rituximab combined with lenalidomide is an active initial treatment for patients with FL requiring therapy. The very high 3-year OS rates in both arms indicates that chemotherapy-free regimens should be further investigated.
Abstract
Background: The randomized phase-2 trial SAKK 35/10 was conducted by the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research (SAKK) and the Nordic Lymphoma Group (NLG) to compare the activity of single-agent rituximab versus rituximab plus lenalidomide in the first-line treatment of symptomatic follicular lymphoma (FL). The results of primary endpoint (complete remission [CR/CRu] at week 23) assessment were previously reported, showing that addition of lenalidomide to rituximab results in a significantly higher CR/CRu rate at the expected cost of increased but manageable toxicity (Kimby et al. Blood 2014.124 (21):799; Zucca et al. Hematol Oncol 2015. 33(s1): 105). Here we report the first analysis of secondary endpoints, progression-free survival (PFS), time to next anti-lymphoma treatment (TTNT), CR duration, as well as CR/CRu rate at 30 months (CR30).
Methods: 154 patients (pts) with grade 1 to 3a FL, untreated and in need of systemic therapy, were randomized to receive either rituximab (375mg/m2 at week 1, 2, 3, 4, 12, 13, 14 and 15) or rituximab (same schedule) plus lenalidomide (15 mg daily, from 14 days before the first until 14 days after the last rituximab administration). The sample size was calculated to allow the detection of a 20% increase of the CR/Cru rate with 90% power and type I error 0.10; a one-sided Z-test for proportions was used to compare the two arms. Treatment was discontinued in pts who did not achieve at least a 25% reduction in the sum of products of tumor diameters at week 10. Primary and secondary endpoints were defined according to the NCI international standardized criteria (Cheson et al 1999).
Results: 77 pts (median age 63 years, 52% with stage IV and 47% with poor-risk FLIPI score) were allocated in the single-agent rituximab arm and 77 (median age 61 years, 48% with stage IV and 47% with poor-risk FLIPI score) in the combination arm. A higher CR/CRu rate in the combination arm was documented both by the investigator assessment (36% vs 25%) and by the independent response reviewers of CT scans (61% vs. 36%). Adverse events of grade ≥3 were more common (56% vs 22% of pts) in the combination arm, including neutropenia (23% vs 7%). At a median follow up of 3.1 years, a longer CR duration was seen for the pts in the combination arm (median not reached vs 2.3 years) as well as a longer PFS (median not reached vs. 2.3 years), these differences were not statistically significant. The CR30, recently identified as a reliable surrogate of PFS (Sargent et al. Hematol Oncol 2015. 33(s1): 166), was significantly improved by the addition of lenalidomide to rituximab (42% vs 19%, p=0.001). Moreover, TTNT was significantly longer with the combination (median not reached vs 2.1 years, p=0.02) [Figure1]. Overall survival rates at 3 years were 93% and 92%, respectively.
Conclusions: The SAKK 35/10 randomized trial confirmed that lenalidomide plus rituximab is an active and feasible initial treatment for FL pts in need of therapy. Addition of lenalidomide significantly increased the CR/CRu rate at week 23 (primary endpoint) and was maintained throughout 30 months. Although the trial was not powered to detect survival differences (secondary endpoints), a significantly better TTNT and a trend towards prolonged PFS and CR duration was seen in the combination arm. The excellent overall survival in both arms suggests that chemotherapy-free strategies should be further explored.
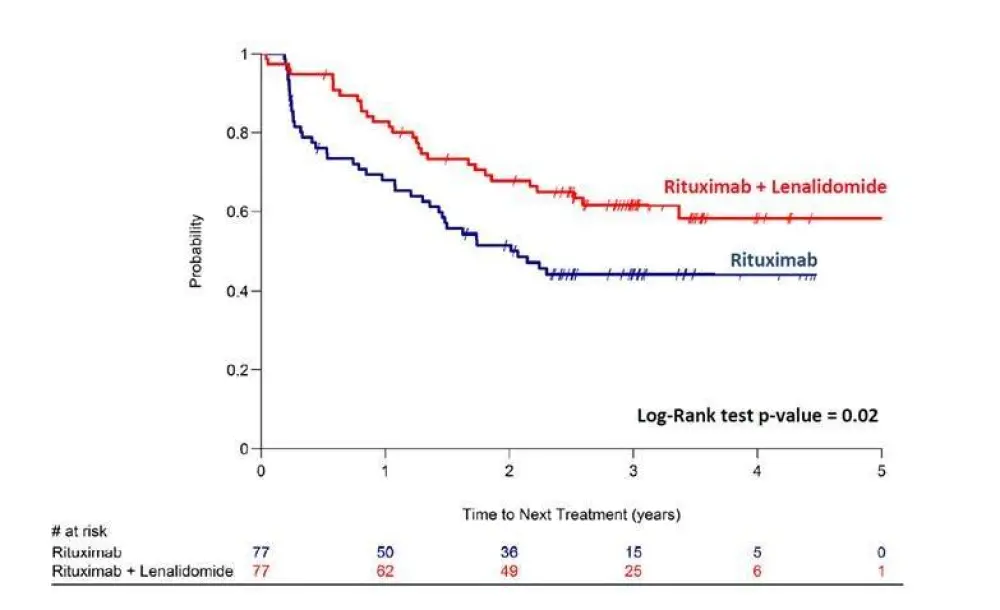
Figure 1. Time to next anti-lymphoma therapy by treatment arm
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content

