All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the Lymphoma Coalition.
The lym Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lym Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lym and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lymphoma & CLL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AbbVie, BeOne Medicines, Johnson & Johnson, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Nurix Therapeutics, Roche, Sobi, and Thermo Fisher Scientific and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, and Pfizer. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lymphoma & CLL content recommended for you
SWOG S1826: Nivolumab-AVD vs brentuximab vedotin-AVD in patients with newly diagnosed advanced-stage cHL
Featured:
Brentuximab vedotin (Bv), an anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate, has demonstrated improved survival outcomes in adult and pediatric patients with classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma (cHL); however, treatment with Bv is associated with increased toxicity, with most pediatric patients receiving radiation therapy and many experiencing disease progression.
In contrast, CheckMate 205 (NCT02181738), a phase II trial evaluating nivolumab plus doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (N-AVD), demonstrated promising safety and efficacy in patients with newly diagnosed HL.2 It was therefore hypothesized that N-AVD has potential as a new standard-of-care treatment for pediatric and adult patients with advanced cHL.
Previously, the Lymphoma Hub spoke to Hun Lee about the safety and efficacy of Bv, nivolumab, doxorubicin, and dacarbazine for advanced stage cHL. During the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, Herrera presented results from SWOG S1826 (NCT03907488) comparing N-AVD vs Bv-AVD in patients with newly diagnosed advanced-stage cHL. Below, we summarize the key findings.
Study design1
This phase III randomized trial enrolled adult and pediatric patients who were
- ≥12 years of age;
- had stage 3–4 de novo HL;
- were HIV+, if controlled;
- left ventricular ejection fraction ≥50%;
- creatinine clearance ≥30 mL/min;
- total bilirubin ≤2 × upper limit normal (ULN); and
- aspartate aminotransferase/alanine transaminase ≤3 × ULN.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive N-AVD or Bv-AVD (Figure 1). The primary endpoint for this secondary interim analysis was progression-free survival (PFS), with the assumption from the initial analysis that 2-year PFS would be 84% for Bv-AVD and 90% for N-AVD with a final analysis reporting 179 events.
Figure 1. Study design*
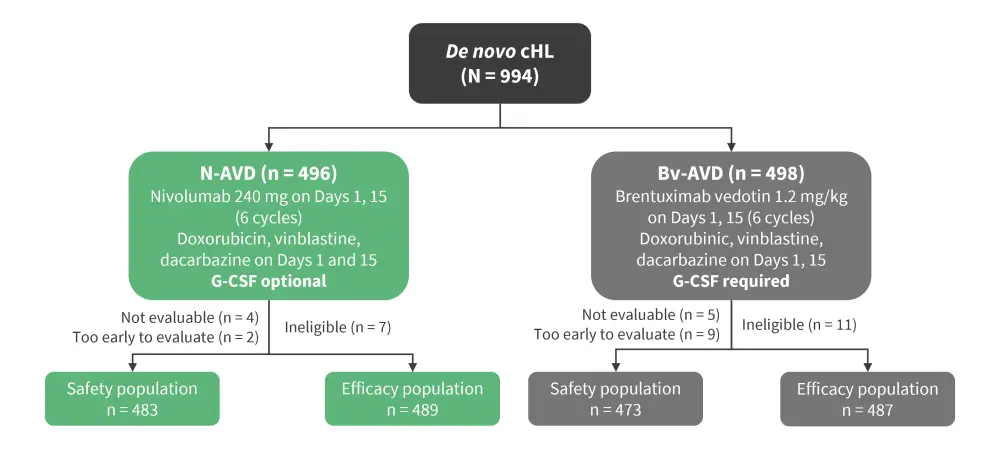
Bv-AVD, brentuximab vedotin-doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine; cHL, classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma; G-CSF, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; N-AVD, nivolumab-AVD.
*Adapted from Herrera.1
Results1
A total of 976 patients with newly diagnosed cHL were included. The baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Baseline patient characteristics*
|
Baseline characteristic, % (unless otherwise stated) |
N-AVD (n = 489) |
Bv-AVD (n = 487) |
|
Median age, years |
27 |
26 |
|
12–17 |
25 |
24 |
|
18–60 |
66 |
66 |
|
≥61 |
9 |
10 |
|
Female |
45 |
44 |
|
Stage |
|
|
|
III |
38 |
34 |
|
IV |
62 |
65 |
|
IPS score |
|
|
|
0–3 |
68 |
68 |
|
4–7 |
32 |
32 |
|
Bulky disease >10 cm |
32 |
27 |
|
HIV+ |
2 |
1 |
|
Bv-AVD, brentuximab vedotin-doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; IPS, International Prognostic Score; N-AVD, nivolumab-AVD. |
||
Efficacy1
- With a median follow-up of 12.1 months, 1-year PFS was higher in N-AVD vs Bv-AVD treated patients (94% vs 86%, respectively).
- Survival benefits were consistent across subgroups where age, IPS, stage and symptoms did not impact PFS.
- Event-free survival was higher in N-AVD vs Bv-AVD treated patients (91% vs 84%, respectively).
Safety1
- Fatigue, gastrointestinal, and hematological toxicities were the most common adverse events (AEs), with Grade ≥3 AEs including neutropenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia (Figure 2).
- Growth factor use and bone pain was lower in the N-AVD vs Bv-AVD arm (54% vs 95% and 8% vs 20%, respectively).
- Infectious toxicity was not increased in the N-AVD arm compared with the Bv-AVD arm:
- febrile neutropenia: 5% vs 7%;
- sepsis: 2% vs 3%; and
- infections: 5% vs 8%, respectively.
- Rates of immune-related adverse events were low in both treatment groups, with ALT increased, AST increased, and hypothyroidism/hyperthyroidism reportedly higher in N-AVD vs Bv-AVD treated patients (32% vs 41%, 25% vs 35%, and 7/3% vs 1%, respectively) while peripheral neuropathy (any grade) was more common in the Bv-AVD arm.
- Overall, early treatment discontinuation was lower in the N-AVD versus Bv-AVD arm (8% vs 12%, respectively). Radiotherapy was received by two and four patients in the N-AVD and Bv-AVD arm, respectively.
- Numerically, fewer deaths were reported in the N-AVD arm (n = 2) vs Bv-AVD arm (n = 8).
Figure 2. Grade ≥3 AEs*
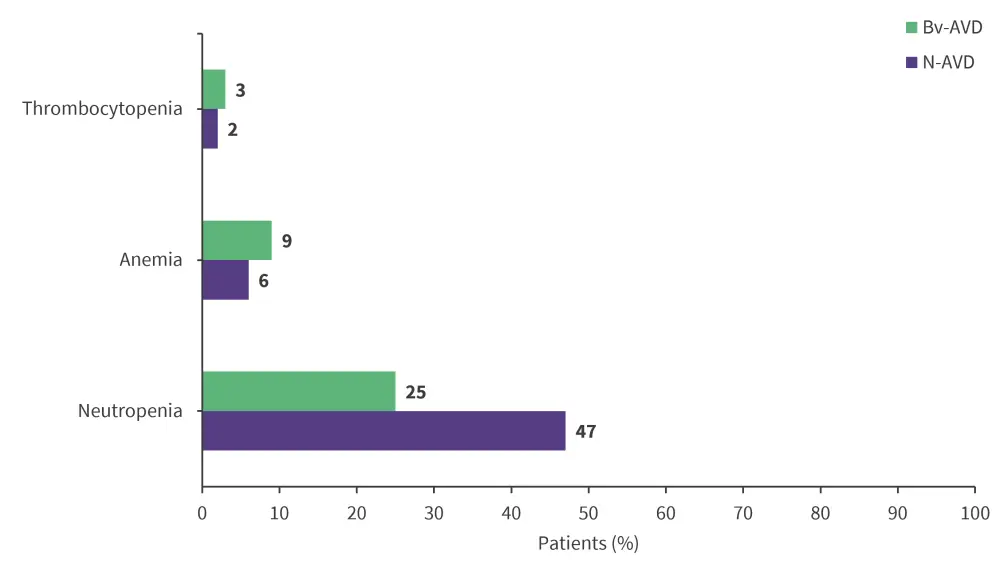
AE, adverse event; Bv-AVD, brentuximab vedotin- doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine; N-AVD, nivolumab-AVD.
*Adapted from Herrera.1
Conclusion
These findings demonstrated that N-AVD improved PFS and was well tolerated in both pediatric and adult patients with newly diagnosed cHL compared with Bv-AVD. Overall, with <1% of patients receiving consolidative radiotherapy and consistency across subgroups, these results suggest N-AVD could be a new standard therapy for advanced stage cHL. Follow-up data are required to confirm OS, safety, and patient-reported outcomes.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content


 Alex Herrera
Alex Herrera