All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the Lymphoma Coalition.
The lym Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lym Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lym and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lymphoma & CLL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AbbVie, BeOne Medicines, Johnson & Johnson, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Nurix Therapeutics, Roche, Sobi, and Thermo Fisher Scientific and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, and Pfizer. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lymphoma & CLL content recommended for you
CheckMate 436: Nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin for R/R PTCL and CTCL
Patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) have poor outcomes.1 Overexpression of PD-L1 and CD30 is often observed in patients with PTCL (15–41% and 46–100%, respectively) and CTCL (27–73% and 47–76%, respectively).1 Nivolumab is a checkpoint inhibitor that targets PD-1/PD-L1 binding, and brentuximab vedotin (BV) is an anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate.1 BV was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of patients with CTCL, based on results from the phase III ALCANZA trial (NCT01578499) which were previously reported by the Lymphoma Hub.1
Zinzani et al.1 recently published an analysis of nivolumab plus BV in PTCL and CTCL cohorts of the phase I/II CheckMate 436 trial (NCT02581631) in Blood Advances, which we summarize below.
Study design1
- The phase I/II CheckMate 436 trial included adult patients with R/R PTCL or CTCL who had received ≥1 prior line of therapy.
- Patients received 240 mg nivolumab on Day 8 of Cycle 1, and Day 1 of each subsequent 3-week cycle, plus 1.8 mg/kg BV intravenously on Day 1 of each cycle until progressive disease or unacceptable toxicity.
- The primary endpoint was overall response rate.
Key findings1
Patient characteristics
- In total, 62 patients with PTCL (n = 33) and CTCL (n = 29) received treatment
- The median age was 60 years and 61 years in the PTCL and CTCL cohorts, respectively
Efficacy
- In the PTCL and CTCL cohorts:
- the median follow-up was 9.6 months and 24.4 months, respectively;
- the median duration of response was 4.6 months and 27.0 months, respectively;
- median progression-free survival was 4.3 and 15.6 months, respectively; and
- median overall survival was 11.1 and 37.2 months, respectively.
Response rates for the PTCL and CTCL cohorts are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Response rates after nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin treatment*
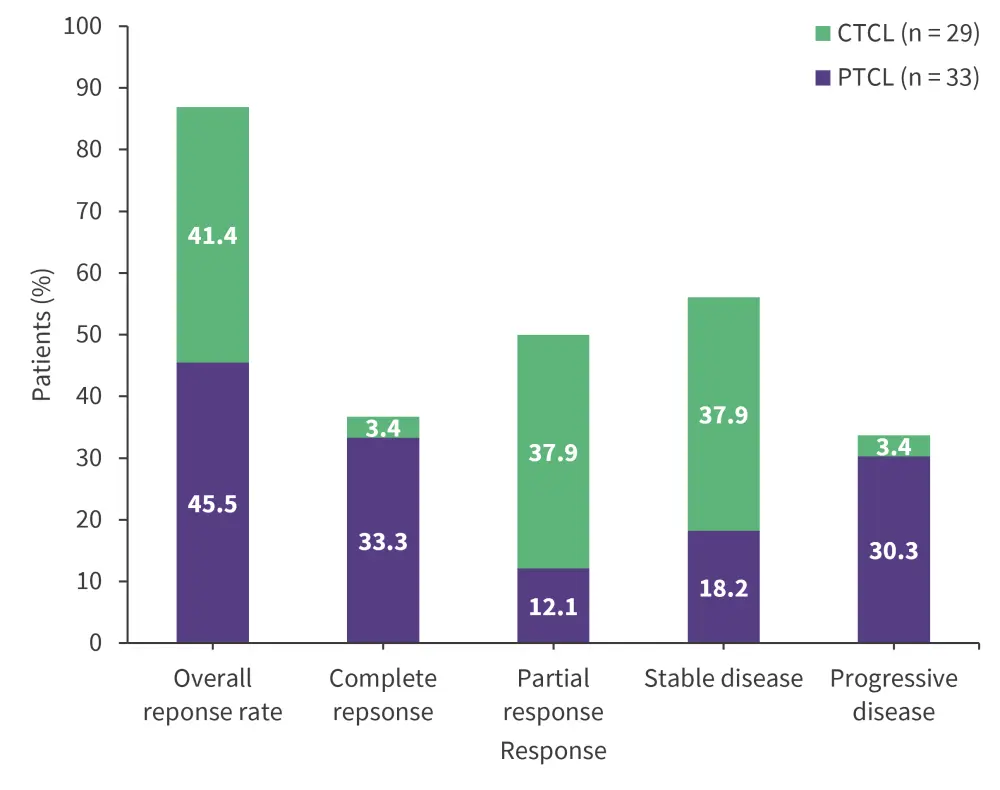
CTCL, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; PTCL, peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
*Data from Zinzani, et al.1
Safety
- In the PTCL cohort:
- Overall, 84.8% of patients experienced any grade treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), most commonly fatigue (24.2%)
- Grade 3/4 TRAEs occurred in 45.5% of patients, most commonly neutropenia (15.2%)
- In total, one patient experienced Grade 5 treatment-related pneumonitis
- In the CTCL cohort:
- Overall, 89.7% of patients experienced any grade TRAEs, most commonly peripheral neuropathy (27.6%).
- Grade 3/4 TRAEs were reported in 44.8% of patients, of which 13.8% were skin-related.
- Overall, 40 deaths were reported in the PTCL (n = 26) and CTCL (n = 14) cohorts, most commonly due to progressive disease (n = 21 and n = 11, respectively). One death was due to treatment-related Grade 5 pneumonitis in the PTCL cohort.
| Key learnings |
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content




