All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the Lymphoma Coalition.
The lym Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lym Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lym and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lymphoma & CLL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AbbVie, BeOne Medicines, Johnson & Johnson, Roche and sobi, and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte and Lilly. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lymphoma & CLL content recommended for you
iwCLL 2017 | Ibrutinib inhibits CXCR4 expression/function and causes CLL cell death by neglect
The second session at this year’s iwCLL was titled “Role of Non-Leukemic Cells and the Microenvironment in CLL Development”, and was jointly chaired by Silvia Deaglio (University of Turin, Torino, Italy) and Christopher Pepper (Cardiff University, Wales, UK).
“Trafficking Between Lymphoid Microenvironments in CLL Survival and Growth” was a talk presented during this session by Jan A. Burger from the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, USA.
The talk began with a brief overview of CLL trafficking and tissue homing:
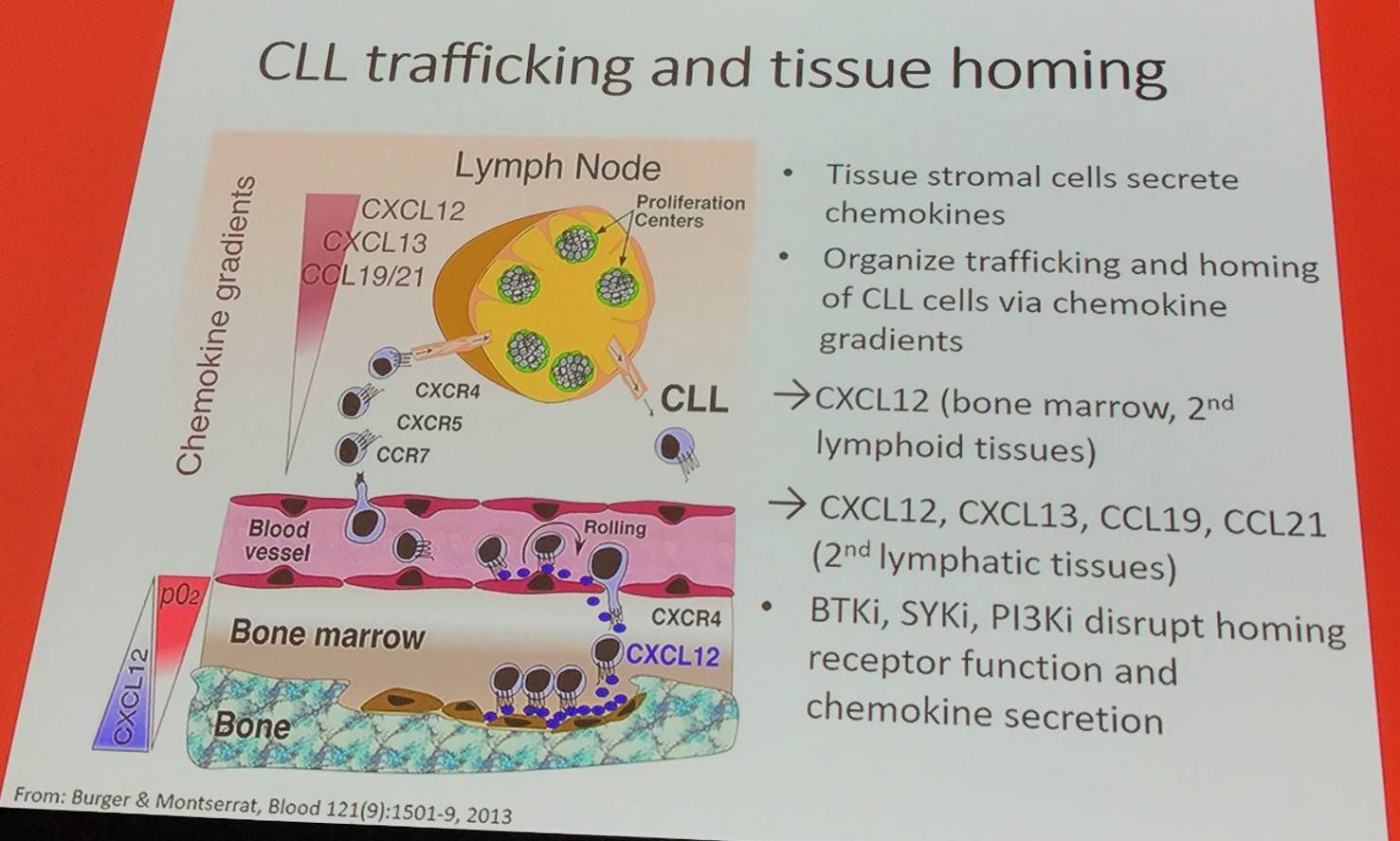
In addition, it has been reported that CXCL12 (SDF-1) is expressed and secreted by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (Burger et al. 1999).
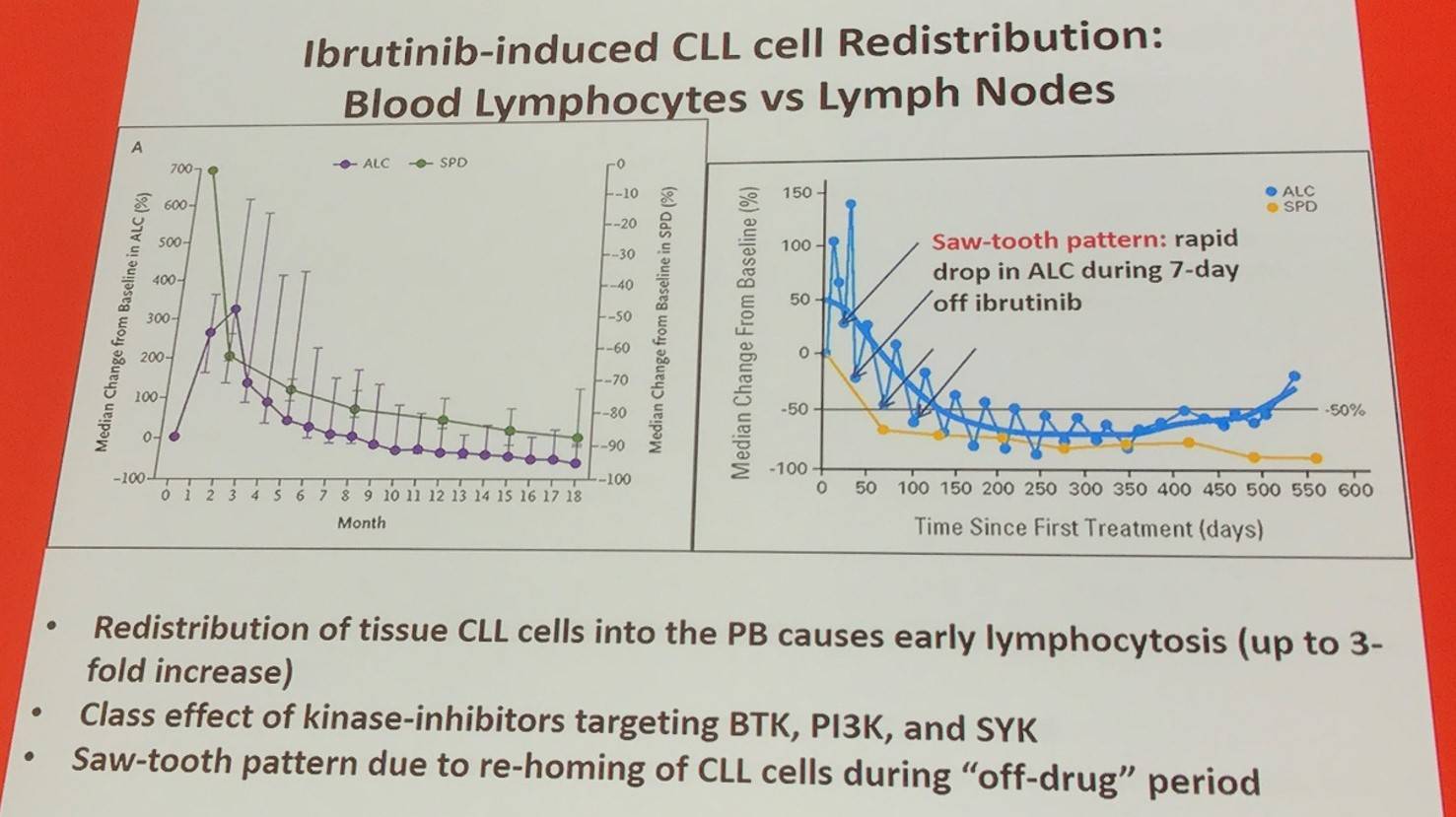
Ibrutinib has been reported to inhibit CLL cell chemotaxis (Ponader et al. 2012; De Rooij et al. 2012). Moreover, ibrutinib reduces sCXCR4 expression and CXCR4 signaling. The release of leukemia cells from lymphoid tissues by ibrutinib is because of the lowered expression of CXCR4 on the cell membrane and blocking CXCR4 signal transductions after ligand binding (Chen et al. 2016).
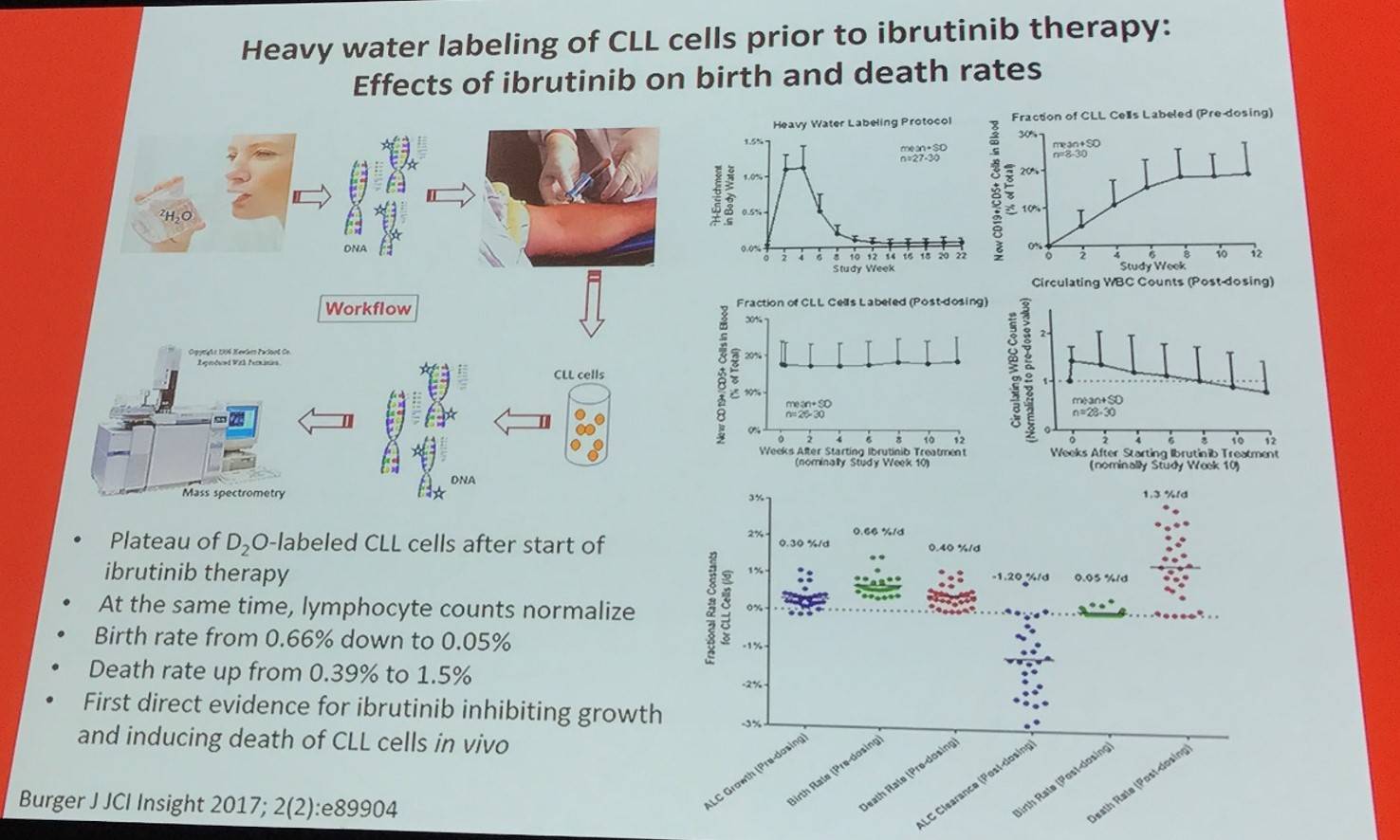
It appears that ibrutinib has a dual action that inhibits proliferation and accelerates CLL cell death via two different mechanisms:
- Acutely causes death of BCR signaling-dependent CLL cells (mostly in tissues)
- Chronically deprives blood CLL cells from other tissue survival signals
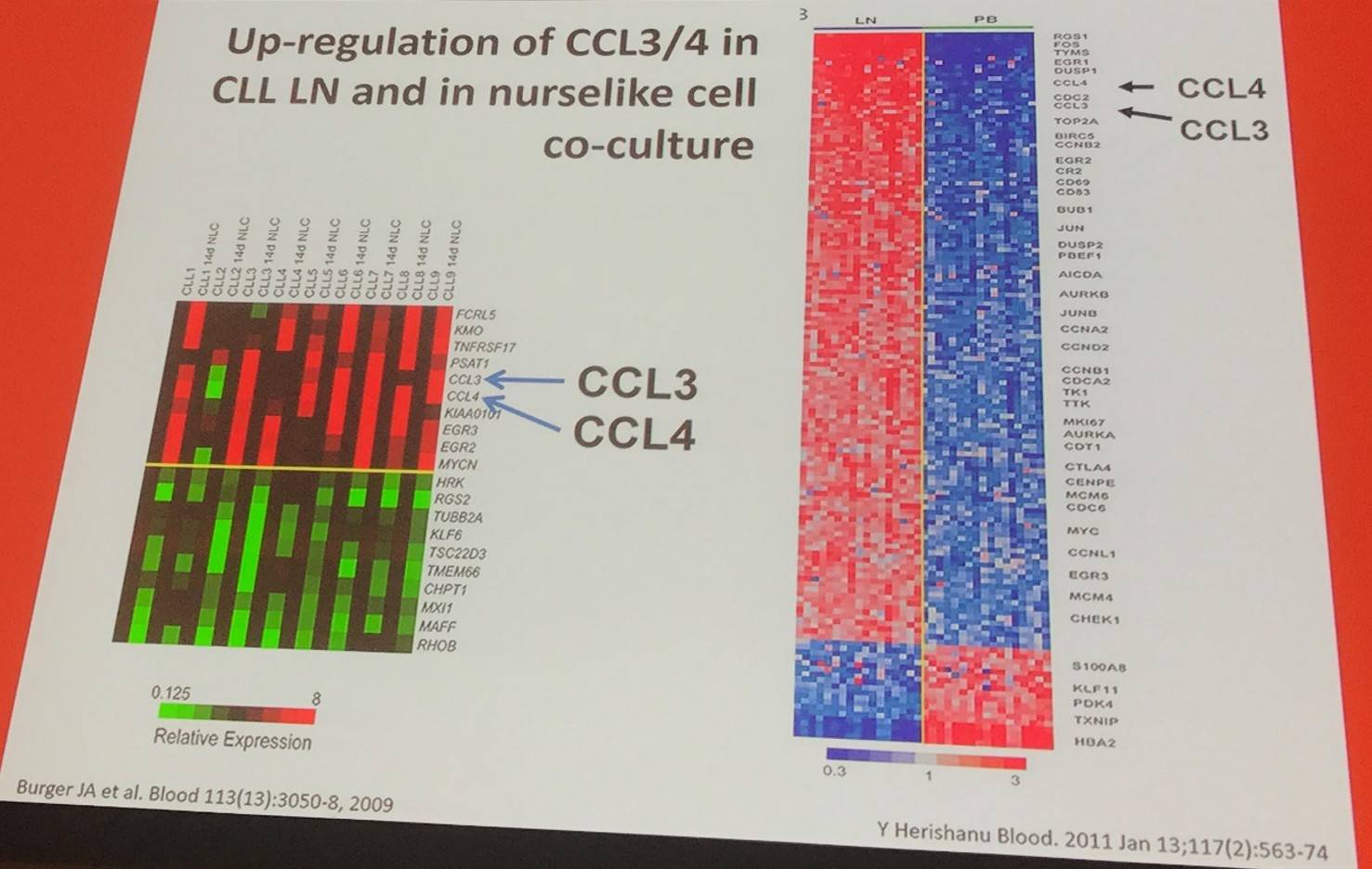
In addition, BCR triggering resulted in robust CCL3/CCL4 protein secretion by CLL cells (Burger et al. 2009).
In a model using peripheral blood CLL cells that mimicked the lymph node microenvironment, IgM signaling induced extended ERK kinase activation and promoted CLL cell survival, secretion of CCL3/CCL4, and BCL6 downregulation. On the other hand, IgD signaling induced activation of HS1 and F-actin polymerization, resulting in swift internalization of receptors and failure to support downstream responses (including CLL cell survival and chemokine secretion). When CLL cells were co-cultured with nurselike cells, downmodulation of IgM and IgD BCRs, activation of HS1 and ERK, chemokine secretion, and decreased expression of BCL6 downregulation were reported. Ibrutinib inhibits IgM and IgD signaling (Hacken et al. 2016).
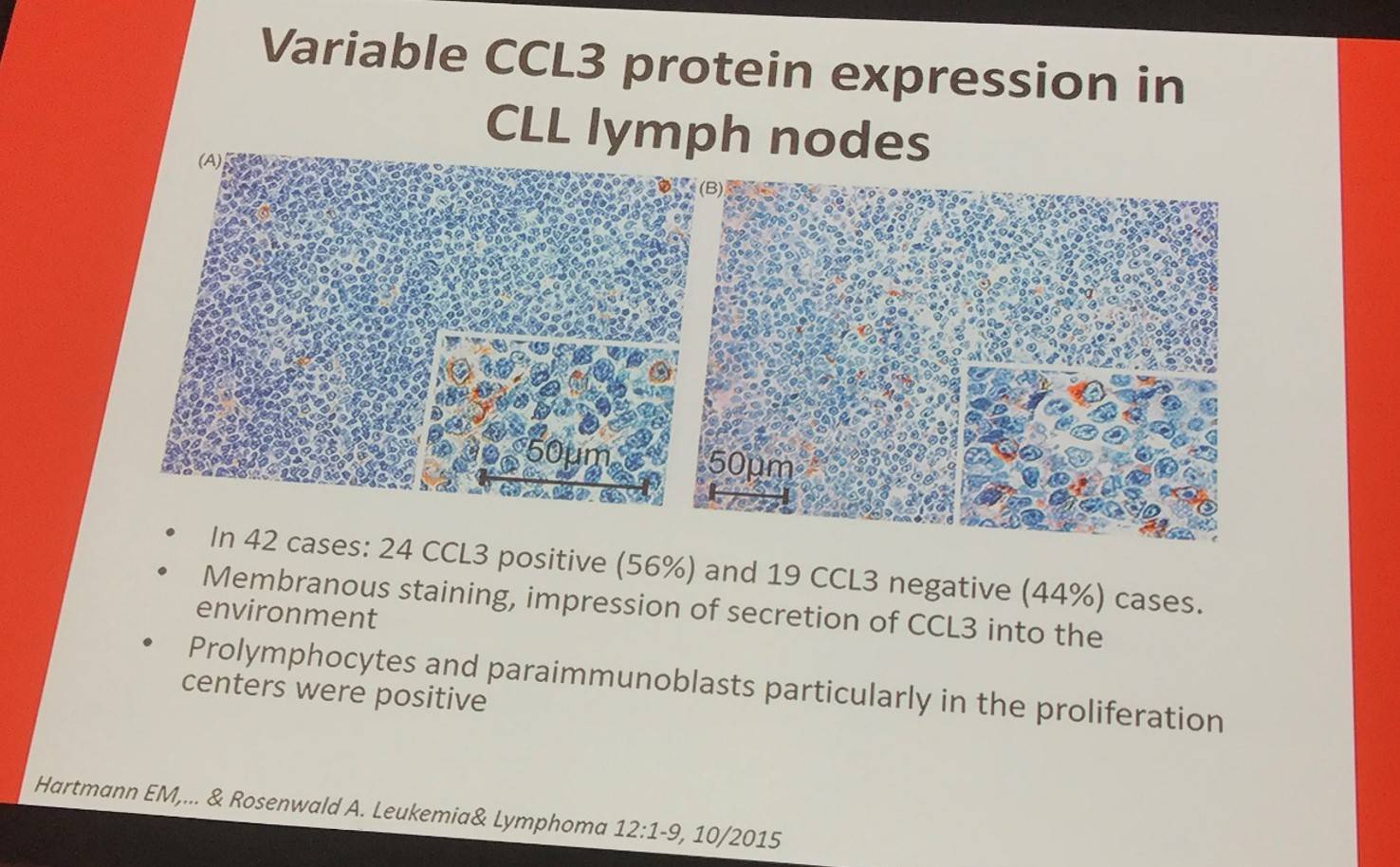
CCL3 positive cases show more prominent T-cell infiltrates (CD3, CD4, and CD8) as well as higher numbers of CD57 positive cells and a higher proliferation fraction (Ki-67-pos).
Jan Burger finished the talk by presenting a final summary slide:

References
Your opinion matters
In your experience, when do most CRS/ICANS events occur after lisocabtagene maraleucel infusion?

