All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit the Lymphoma Coalition.
The lym Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the lym Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The lym and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The Lymphoma & CLL Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by AbbVie, BeOne Medicines, Johnson & Johnson, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Nurix Therapeutics, Roche, Sobi, and Thermo Fisher Scientific and supported through educational grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Lilly, and Pfizer. Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View lymphoma & CLL content recommended for you
Symposium | First-line BTK inhibitors in clinical practice: Case study clinic
Featured:
Do you know... In the phase III CLL13 study, which of the following treatments had better 3-year PFS in patients with CLL and unmutated IGHV status?
During the Lymphoma Hub virtual symposium on October 23, 2024, entitled Customizing first-line Bruton‘s tyrosine kinase (BTK) for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), Francesc Bosch, Vall d'Hebron Barcelona Hospital Campus, Barcelona, ES, shared a clinical case report and discussed treatment optimization strategies with BTK inhibitors in first-line CLL.
Symposium | First-line BTK inhibitors in clinical practice for CLL: Case study clinic
Bosch began by presenting a clinical case of a 73-year-old fit male with a medical history of hypertension who developed asymptomatic CLL (Figure 1). Bosch discussed the treatment approach, including key diagnostic steps such as imaging assessment, and the impact of various factors such as age, fitness, mutational status, and international prognostic index score, when selecting a treatment option. He also considered the latest data from clinical trials of BTK inhibitors in first-line CLL by highlighting long-term outcomes from the CAPTIVATE (Figure 2), GLOW, ELEVATE-TN, RESONATE-2, SEQUOIA, CLL13, and CLL14 trials, and described the deep and durable responses found with BTK inhibitors, particularly in patients with high-risk features including unmutated IGHV and del(17p)/TP53mut.
Figure 1. Clinical case of a 73-year-old male with CLL
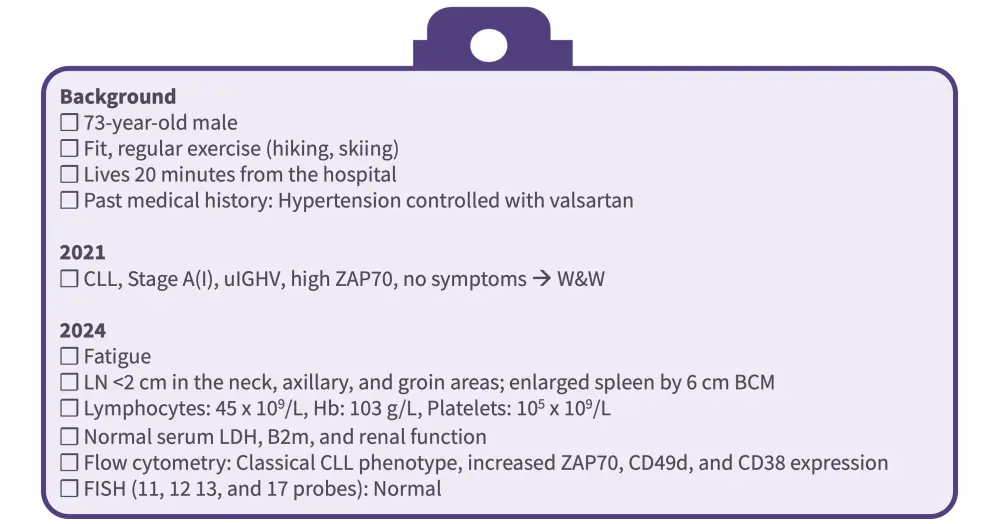
B2m, β2 microglobulin; BCM, below costal margin; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization; Hb, hemoglobin; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; LN, lymph node; uIGHV, unmutated IGHV; W&W, watch and wait.
Figure 2. Key outcomes from the CAPTIVATE trial in high-risk CLL: FD + MRD cohorts*
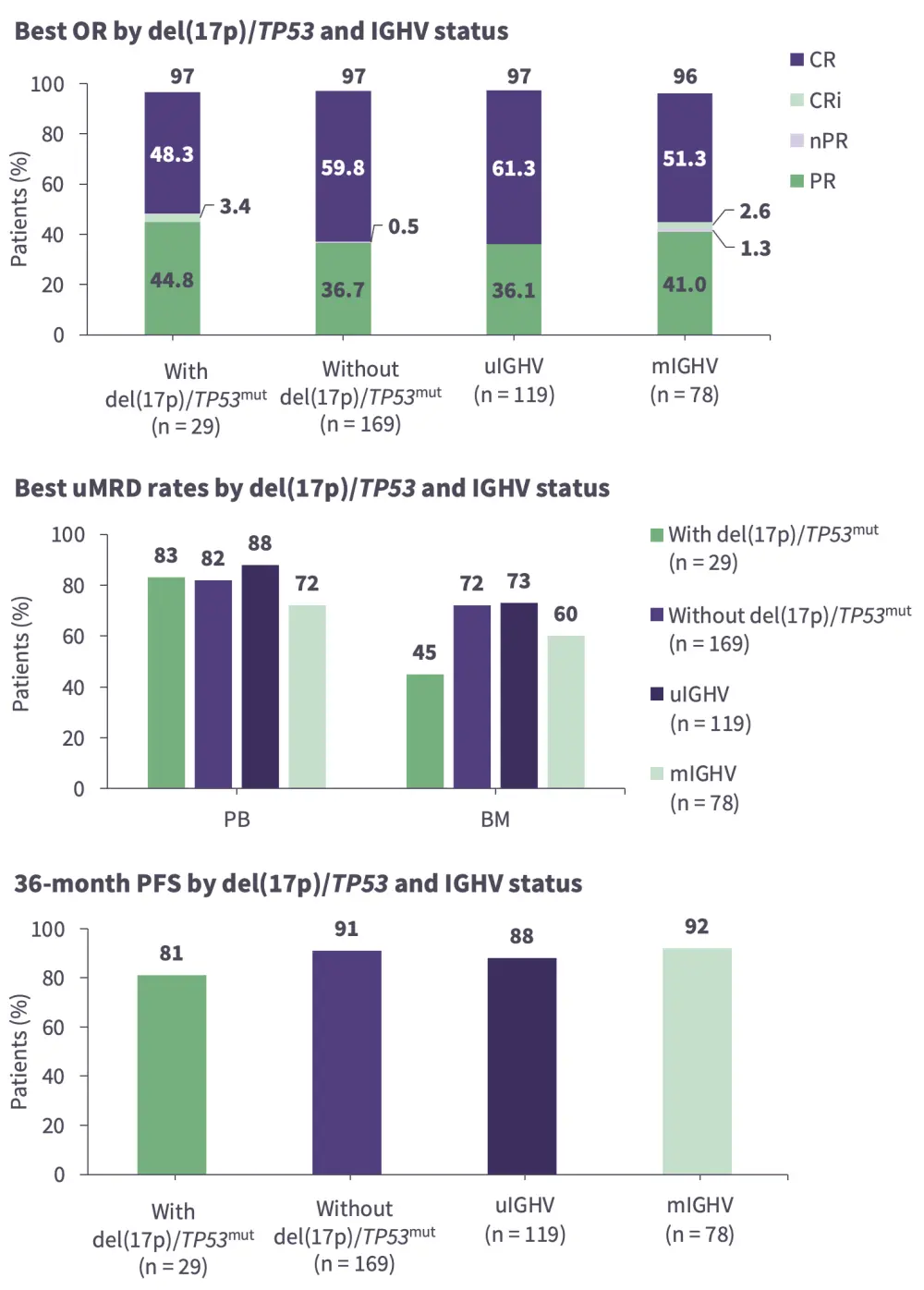
BM, bone marrow; FD, fixed-duration; CR, complete response; CRi, complete response with incomplete BM recovery; IGHV, immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region; m, mutated; MRD, measurable residual disease; mut, mutation; nPR, nodular PR; OR overall response; PB, peripheral blood; PFS, progression-free survival; PR, partial response; u, unmutated; uMRD, undetectable MRD.
*Data from Allan, et al. 1
Key takeaways:
- TP53mut and IGHV molecular status should be considered when selecting treatments for patients with CLL.
- Covalent BTK inhibitors demonstrate high efficacy in patients with unmutated IGHV.
- B-cell lymphoma-2 inhibitors and anti-CD20 combinations exhibit lower efficacy in patients with unmutated IGHV.
- Fixed-duration ibrutinib + venetoclax demonstrates efficacy in patients with high-risk CLL (with del(17p)/TP53mut and/or unmutated IGHV), although longer follow-up is needed.
This independent educational activity was supported by an educational grant from Janssen Biotech, Inc., administered by Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC. All content was developed independently by SES in collaboration with the faculty. The funder was allowed no influence on the content of this activity.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content


 Francesc Bosch
Francesc Bosch


